Age & Ovarian Cancer: Understanding Your Risk Throughout Life
Understanding ovarian cancer risk can be a profound aspect of women’s health awareness. It is not a condition that pertains to any one age group, but rather, its potential presence ripples across the milestones and changes that every woman experiences throughout her life.
From the onset of menstruation to the cessation of menses, and through every year in between, a woman’s susceptibility to ovarian cancer shifts.
This blog deep-dives into the topic, shedding light on how ovarian cancer risk is intricately linked to the different stages of life. For you, this knowledge is essential for making informed decisions about your health.
Ovarian Cancer Basics
Ovarian cancer is a malignancy that begins in the ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system. The ovaries, which are responsible for producing eggs and female hormones, can develop various types of tumors. Some of these are cancerous, while others are non-cancerous and never spread beyond the ovaries.
-
Ovarian Cancer Types
The cell type where the cancer starts determines the type of ovarian cancer. The most common type is epithelial ovarian cancer, which starts in the cells on the surface of the ovary. Other rarer types include germ cell tumors, which start from the cells that produce eggs, and sex cord-stromal cell tumors that come from the cells that release female hormones.
-
Stages and Grades of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is staged from I to IV, depending on how far it has spread. Grade 1 tumors are less aggressive compared to higher-grade tumors which are more likely to spread. These determinants play a critical role in guiding treatment plans and predicting outcomes.
What are the Odds of Getting Ovarian Cancer by Age?
Ovarian cancer risk is a dynamic factor that evolves as a woman advances through her life. Understanding this progression is key to proactive healthcare management.
-
Young Adults: A Rare Occurrence
For young adults, ovarian cancer is rare, yet can still occur. It is the primary cause of gynecologic cancer death, often due to delays in diagnosis related to its silent symptom profile.
-
Women in their Reproductive Years: Mid-Life Watchfulness
During this stage, ovarian cancer is more likely to develop but is usually diagnosed in a less advanced stage, which can lead to more successful treatment.
-
Perimenopausal and Menopausal Women: The Likely Years
This period sees the highest incidence of ovarian cancer diagnoses. The transition into and through menopause is a critical time to monitor for changes in health and possible cancer symptoms.
-
Elderly Women: A Heightened Risk
Though the incidence of all cancers increases with age, ovarian cancer still ranks high among the cancers that affect older women. However, the availability of screening and the prioritization of health play significant roles in early detection and management.
What Causes Ovarian Cancer at a Young Age?
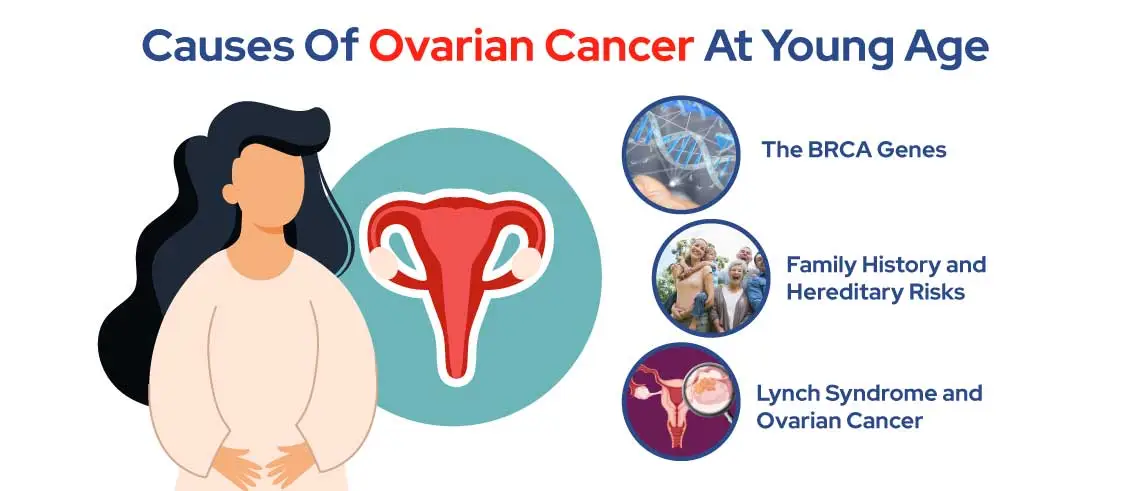
While ovarian cancer is more common in older women, it does occur in younger females. Genetic factors like BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations significantly raise the risk, as well as family history and Lynch syndrome.
-
The BRCA Genes and Their Implication
Inherited mutations in the BRCA genes lead to a substantially increased risk of breast and ovarian cancers, especially at a young age. Understanding one’s genetic predispositions is critical for early intervention and preventive measures.
-
Family History and Hereditary Risks
Women with a strong history of ovarian or breast cancers in their families face an elevated risk. It’s essential to communicate and document family health history, allowing for proactive and personalized care plans.
-
Lynch Syndrome and Ovarian Cancer
Lynch Syndrome, a hereditary condition, increases the risk of several cancers, including ovarian cancer. Genetic counseling could shed light and offer pathways for prevention and early detection.
Who is at High Risk for Ovarian Cancer?
High-risk populations can benefit from tailored risk reduction strategies and more frequent screenings.
-
Understanding and Mitigating Genetic Risks
Genetic counseling and testing can help identify individuals with high-risk gene mutations. Lifestyle changes, preventive surgeries, and close monitoring are often recommended for these individuals.
-
Endometriosis and Ovarian Cancer
Endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus is found outside the uterus, increases ovarian cancer risk slightly. It reinforces the importance of considering individual health history when evaluating cancer risk.
-
Environmental and Lifestyle Risk Factors
Certain factors such as obesity, smoking, and the use of fertility drugs may slightly increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Adopting healthy lifestyles can contribute to reducing this risk.
How to Prevent Ovarian Cancer?
Proactive measures can reduce the risk of ovarian cancer, especially in high-risk populations.
-
Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise and a balanced diet can contribute to lowering the risk of ovarian cancer. These simple changes form a protective web against not just ovarian cancer but other health issues.
-
Regular Screenings
For women with higher risk factors, such as a family history of ovarian cancer, more frequent screenings may be recommended. These can include pelvic exams, transvaginal ultrasounds, and blood tests to monitor cancer-related markers.
-
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can be a powerful tool in cancer risk assessment. It is a direct and individualized view into potential health risks, enabling informed decisions about surveillance and preventive strategies.
Silent Signs of Ovarian Cancer
Signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer can be subtle and easily overlooked, particularly in the early stages.
-
Persistent bloating
Ovarian cancer can cause a buildup of fluid in the abdominal cavity, leading to persistent bloating or an increase in abdomen size.
-
Pelvic or abdominal pain
Pain in the pelvis or the lower part of the abdomen can signal ovarian cancer, especially in women over the age of 40.
-
Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
Some women with ovarian cancer experience a loss of appetite and may feel full after eating only a small amount.
-
Changes in bowel or bladder habits
Frequent and urgent urination, constipation, bowel movements, or increased gas can be indicative of advanced ovarian cancer pressing on nearby organs.
-
Other less-common symptoms
Unexplained weight loss, fatigue, back pain, and menstrual irregularities can also be symptoms of ovarian cancer.
Importance of symptom recognition
Recognizing these signs and listening to one’s body is crucial. Early detection improves treatment outcomes, making it vital for women to be aware of these silent symptoms and communicate any changes to their healthcare provider.
How to Check for Ovarian Cancer at Home?
While there is no substitute for professional diagnosis, self-advocacy and awareness can lead to early detection.
1.Monthly self-exams
Regular self-examinations, especially when undertaken monthly, can enable women to recognize changes in their bodies more readily.
2.Understanding Normal vs Not-Normal
Becoming familiar with your own body and recognizing what is ‘normal’ for you makes it easier to discern potentially concerning changes.
3.Prompt consultation with a Gynecologist
If any suspicious symptoms are detected, prompt consultation with a gynaecologist for a thorough evaluation and testing is essential.
Conclusion
Understanding your specific ovarian cancer risks at every life-stage empowers you to take control of your health, ensure early detection, and potentially save your life. Kolhapur Cancer Center is committed to providing state-of-the-art care and support for women at every age.
Contact us for more information about ovarian cancer risk, prevention, and screening. With your proactive approach, a healthier and more secure future awaits.
Previous article
What is the Life Expectancy for Esophageal Cancer?
Next article
What Is the Survival Rate for Colon Cancer?

