Ovarian Cancer: Debunking the Myths to Save Lives
The battle against ovarian cancer is complex. Beyond the medical challenges, there is a web of undecipherable myths that can lead to delayed diagnosis and, potentially, fatal outcomes. In an arena where knowledge is power, separating truth from conjecture is crucial. For women’s health and the fight against ovarian cancer, it’s time to debunk the myths and arm ourselves with cold, hard facts.

Setting the Stage
Ovarian cancer is often referred to as the “silent killer,” a term teeming with dread and fear. Yet, underneath these unnerving statistics lies a silver lining — the power of knowledge. Despite its stealthy nature, ovarian cancer does offer some tell-tale signs, and debunking the myths can play a pivotal role in saving lives.
Common Myths Surrounding Ovarian Cancer
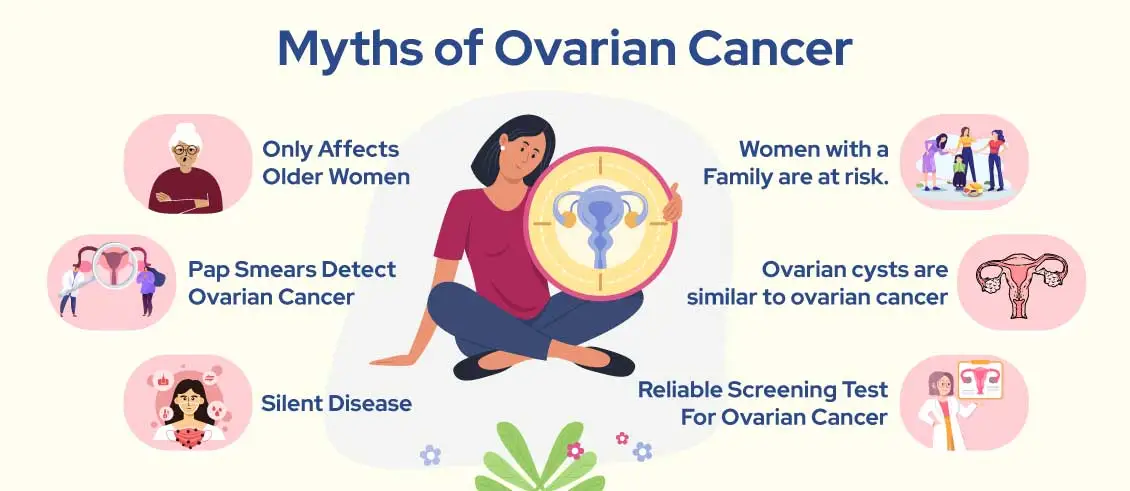
Here, we dissect three prevalent misconceptions and unravel the truths behind the smokescreen of misinformation.
Myth 1: Ovarian Cancer Only Affects Older Women
Many believe ovarian cancer is an older woman’s disease, citing statistics that show elevated risks in post-menopausal women. However, ovarian cancer can strike at any age, directly challenging the misconception that ‘you’re too young’ to worry about it.
The Reality
Age is indeed a risk factor, but ovarian cancer is not exclusive to older women. There’s an increasing recognition of ovarian cancer among women in their 30s and 40s. This myth’s debunking is imperative to ensure early detection and better survival rates, particularly among younger demographics.
Myth 2: Pap Smears Detect Ovarian Cancer
Many believe that regular Pap smear tests, critical for detecting cervical cancer, also screen for ovarian cancer. This misunderstanding can provide a false sense of security concerning ovarian cancer detection.
The Reality
Pap smears do not detect ovarian cancer. They are designed to screen for cervical cancer. For ovarian cancer, there are currently no effective screening tests widely available for women who do not present symptoms.
For those at high risk or who show symptoms suggestive of ovarian cancer, transvaginal ultrasounds and CA-125 blood tests may be recommended by an oncologist. However, these tests are not suitable as general screening tools for all women. Awareness of symptoms and risk factors remains key to early detection and intervention.
Myth 3: Ovarian Cancer is a Silent Disease
There’s a common belief that ovarian cancer symptoms are either mild or non-existent, leading to the problematic assumption that ovarian cancer shows no signs until it’s in an advanced stage.
The Reality
While ovarian cancer symptoms can be subtle and easily confused with other, less serious conditions, they do exist. Bloating, pelvic or abdominal pain, difficulty eating or feeling full quickly, and urinary symptoms are common signs, often present but overlooked until the condition has progressed. Recognising and acting upon these signs is vital for early diagnosis and improved outcomes.
Myth 4: Only Women with a Family History of Ovarian Cancer Are at Risk
Many believe that a family history of ovarian cancer is the main risk factor for developing the disease. This notion leads some women without a known genetic predisposition to underestimate their risk.
The Reality
While having a family history of ovarian cancer does increase your risk, the majority of ovarian cancer cases occur in women without a familial link. Other factors, such as age, the use of hormone replacement therapy, and certain genetic markers, can also elevate a woman’s risk. Awareness and regular screening are important for all women, regardless of their family history.
Additionally, it’s important to note that most ovarian cancers are not hereditary and occur randomly.
Myth 5: Ovarian cysts are similar to ovarian cancer
The Reality
Ovarian cysts are common and usually harmless, while ovarian cancer is a serious disease. Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can form on or inside the ovary, often as part of the normal menstrual cycle. Most ovarian cysts disappear on their own without causing any symptoms or requiring treatment.
On the other hand, ovarian cancer is an abnormal growth of cells in the ovaries that can quickly spread to other parts of the body. It can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early. While some ovarian cancers may present as cysts, most cysts are not cancerous.
Myth 6: There is a reliable screening test for ovarian cancer
The Reality
Unfortunately, there is currently no reliable screening test for ovarian cancer. Pap smears and pelvic exams are not effective in detecting the disease at an early stage. The most common screening method for ovarian cancer is a blood test called CA-125, but it is not specific to ovarian cancer and can give false-positive results.
However, women with a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer, such as those with a family history, may benefit from regular pelvic exams and ultrasounds. It’s important to discuss your personal risk factors with your doctor and determine the best screening plan for you.
Unveiling Facts About Ovarian Cancer
Turning the spotlight on the misbeliefs, we now present the facts that every woman should know.
Fact 1: Ovarian Cancer Can Affect Women of All Ages
While age is a risk factor, ovarian cancer is indiscriminate and can strike younger women. With a rising incidence of ovarian cancer in premenopausal women, age should not be a deterrent to pursuing evaluation for possible symptoms.
Fact 2: Specific Tests Are Needed for Ovarian Cancer Detection
Unlike cervical cancer, ovarian cancer is not easily screened with a routine Pap smear. Specialized imaging tests, such as transvaginal ultrasound and a blood test called CA-125, are often used for diagnosis. These tests are vital for early detection and should be administered with regularity, particularly for women with a family history of ovarian cancer or other risk factors.
Fact 3: Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer Can Be Subtle But Present
Ovarian cancer does exhibit symptoms, though they can be vague and mistakenly attributed to other conditions. Women must pay attention to their bodies, seek medical consultation if they experience persistent symptoms.
Fact 4: Lifestyle Choices and Genetic Factors Play a Role in Risk
Research has demonstrated that certain lifestyle choices and genetic predispositions significantly influence the risk of developing ovarian cancer. For example, individuals with a history of endometriosis, or those who have never been pregnant, may face a higher risk. Furthermore, possessing gene mutations such as BRCA1 or BRCA2 elevates the risk profile. It’s important for women to discuss their genetic history and lifestyle factors with gynecologists to understand their personal risk.
Fact 5: Ovarian Cancer Survival Rates Have Improved
Thanks to advancements in medical research and the development of more effective treatments, the survival rates for ovarian cancer have been steadily improving over the past few decades. Early detection plays a crucial role in survival outcomes, emphasizing the importance of being vigilant and proactive in seeking diagnosis and treatment.
Early Awareness and Detection Of Ovarian Cancer
Awareness is the first line of defense, and only through debunking these myths and sharing the facts can we empower women to take control of their health.
Early detection is a game-changer in the prognosis of ovarian cancer. Dispelling myths and understanding the signs can lead to swifter medical intervention. Regular check-ups and a proactive approach to any persistent symptoms are important steps.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer is still a significant health concern for women worldwide, but with greater awareness and understanding of the facts, we can take steps towards reducing its burden on society.
You must seek medical advice if they experience persistent symptoms, and undergo regular screenings as recommended by the doctor. Together, we can improve survival rates and support those affected by this disease.
For further information, guidance, or support, please do not hesitate to contact Kolhapur Cancer Centre. Our dedicated team of professionals is always ready to provide assistance, answer any queries, and offer the necessary support to those affected by ovarian cancer. We are here to support you every step of the way in your fight against ovarian cancer.
Previous article
What is the Life Expectancy for Esophageal Cancer?
Next article
What Is the Survival Rate for Colon Cancer?

